-
Making the right call: when to use a custom post type
-
Making the right call: when to use a page or a dynamic template
-
Making the right call: when to install a new plugin vs develop from scratch
-
Making the right call: ways to use menus and widgets
Getting your hands on WordPress
How to create content on WordPress
How to develop an efficient website
Content
The first thing you need to know is that content for the web has three main parts: how to access it, how it’s displayed, and how it’s found.
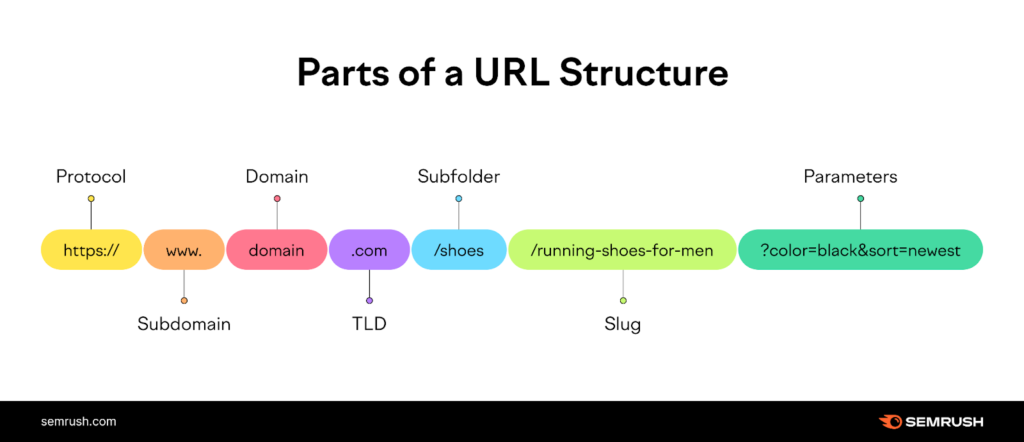
Accessing content on the web demands an URL. And this has up to five components. Imagine a simple website, such as www.google.com.
The “google” is the actual domain, while the “.com” is called the top-level domain. When buying your domain, you have to select both, because you can have google.com.br, google.fr, google.net, and so on.
There are certain top-level domains restricted to certain industries and organizations to facilitate recognition and trust by the general public, such as .gov or .edu.
Login
Accessing this course requires a login. Please enter your credentials below!